- Home
- >
- Software Development
- >
- API Management for Asynchronous APIs – InApps Technology 2025
API Management for Asynchronous APIs – InApps Technology is an article under the topic Software Development Many of you are most interested in today !! Today, let’s InApps.net learn API Management for Asynchronous APIs – InApps Technology in today’s post !
Key Summary
- Overview: The article discusses the importance of API management for asynchronous APIs, focusing on their role in modern applications and how to effectively manage them.
- Key Features of Asynchronous APIs:
- Non-Blocking Communication: Unlike synchronous APIs, asynchronous APIs (e.g., WebSockets, Kafka, AMQP) allow systems to process requests independently, improving responsiveness.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Supports real-time data streaming and event-based interactions, ideal for microservices and IoT.
- Scalability: Handles high volumes of requests efficiently, suitable for distributed systems.
- API Management Strategies:
- Gateway Support: Use API gateways (e.g., Kong, AWS API Gateway) to manage routing, authentication, and monitoring for asynchronous APIs.
- Message Brokers: Integrate with tools like Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ to handle message queues and ensure reliable delivery.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Track performance metrics (e.g., latency, throughput) and errors to ensure system reliability.
- Security: Implement OAuth, JWT, or mutual TLS to secure asynchronous data exchanges.
- Versioning and Documentation: Maintain clear documentation and versioning to manage evolving API contracts.
- Use Cases:
- Real-time applications like chat systems, live notifications, or financial trading platforms.
- IoT systems for processing sensor data streams.
- Microservices architectures requiring decoupled communication.
- Benefits:
- Enhances scalability and performance for high-throughput systems.
- Improves user experience with real-time updates.
- Simplifies integration in distributed, cloud-native environments.
- Challenges:
- Complex setup and management compared to synchronous APIs.
- Requires robust monitoring to handle message delivery failures.
- Ensuring security and compliance in real-time systems.
- Conclusion: Effective API management for asynchronous APIs, leveraging gateways, brokers, and monitoring tools, is critical for building scalable, real-time applications, enabling seamless communication in modern, distributed architectures.
Read more about API Management for Asynchronous APIs – InApps Technology at Wikipedia
You can find content about API Management for Asynchronous APIs – InApps Technology from the Wikipedia website

Menaka Jayawardena
Menaka is an Associate Technical Lead at WSO2, focusing on the research and development of the WSO2 API Microgateway product.
Today, customers increasingly demand access to real-time information like stock prices, train times, etc. Delivering this critical information, as it occurs, is a challenging task for every business. Traditionally, applications polled backend servers to fetch the latest information; however, this proved to be inefficient, as it consumes a significant amount of resources.
APIs should be designed to allow users to receive a stream of events from the service, instead of polling it periodically. Event-driven APIs or asynchronous (async) APIs can be used to meet this requirement — with mission-critical information pushed to client applications at the time of the event.
What Are Async APIs and How Are They Different from REST APIs?
Unlike conventional request/response APIs (e.g., REST and SOAP), asynchronous APIs can send multiple responses to a single request. This can also be in the form of unidirectional or bi-directional communication. There are several protocols that can be used for async APIs, such as Websockets, WebHooks, MQTT, and Server-Sent Events (SSE). Most of these protocols support HTTP at the connection creation stage and use a specific channel to transfer the subsequent messages between the client and the server. Also, conventional HTTP verbs (i.e., GET, POST, PUT, etc.) are not valid for these channels.
Another prominent difference between a REST API and an async API is the usage of an event backbone technology (a message broker such as Kafka or RabbitMQ) and topics. The backend services are registered as event publishers and they publish events on specific topics. Client applications are registered as event subscribers to respective topics, to receive those events published by the publisher services. Upon receiving the events, the client performs the required processing and displays it to the user.
Security, rate limiting, throttling, monetization and analytics are some of the important factors that an organization should focus on when exposing their core business functions as APIs. In order to address these, an enterprise must select the right API management solution. However, since async APIs and REST APIs are conceptually different, several unique challenges arise when using a conventional system for asynchronous APIs. These include incompatibilities with existing security mechanisms and throttling policies, and problems around capturing analytics data. Handling these challenges via a proper API management solution that fully supports event-driven APIs is a must.
Securing Event-Driven APIs
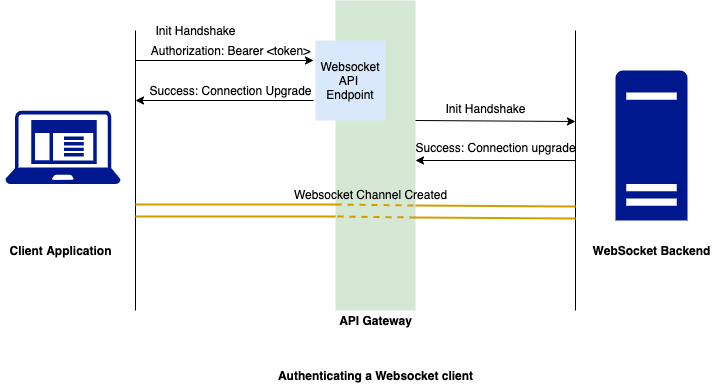
API security can be categorized into authentication and authorization. Authentication describes who can access which resource, while authorization describes whether the authenticated user can perform the specific task. In conventional REST APIs, users can be authenticated using user credentials, access tokens, certificate-based authentication, etc. Also, each resource can also be protected with scopes and each API invocation can be protected too. However, in asynchronous APIs, since there are only topics to which the clients and services are subscribed to and the communication occurs through a dedicated messaging backbone, it is a challenging task to secure APIs.
One possible approach to handle this challenge is by authenticating during the initial HTTP communication. For example, we can secure the initial WebSocket handshake (via HTTP) before creating the connection. It is also possible to enforce authorization by defining whether the client can publish any events or not.
Rate Limiting, Throttling and Monetization
Much of the time, the end goal of any business that exposes APIs for external parties is to generate revenue. For this, the main requirement is the ability to limit the usage of the API (block the access, reduce bandwidth, etc). API management systems support rate limiting and monetization for REST/SOAP APIs, using policies based on the request count (requests per second/minute, bandwidth, etc). When the client exceeds the number of requests allowed, the client is blocked for some time.
Protecting backend services from spikes of requests are also handled via these policies, by introducing a request rate limit. But when it comes to async APIs, servers publish the events and applications are the event subscribers. Therefore, conventional throttling policies cannot be applied, because server-client events need to be considered.
The definition of throttling policies should also be changed. Consider the following:
- Time-based throttling: A client can only be subscribed to the topic for a specific time. After that, the client is disconnected from the server.
- Event count-based throttling: A client can only receive x number of total events. This also can be combined with time-based throttling and create policies (e.g., a count of 10000 events per day).
- Backpressure-based throttling: When the client cannot handle the rate of events it receives, it imposes stress on the gateway to deliver the messages to the client — since it is required to queue the messages and send when the client can accept them. In these situations, the client can be removed from the gateway, to ensure that the gateway is not affected.
Analytics
Analytics plays a vital role in any API-driven business and helps to make informed decisions, by providing details such as the number of API consumers, most-accessed API resources, latencies, identify trends, etc. It should be a mandatory capability supported by an API management product.
In traditional REST/SOAP APIs, an API gateway can capture information such as invoking API resources, backend latencies, geo-locations, etc. These are basically fetched from the request/response headers.
However, when it comes to async APIs, capturing this information becomes much more complex, since there are no HTTP requests or responses. What we do have is a set of topics and subscribers. All the messages are sent through a separate channel (server -> client or client -> server) and the gateway should be able to capture the required information. For each subscriber of the API, the gateway should capture:
- The number of messages being pushed
- The TPS variation overtime
- The number of publishing errors
- Health details about the backend (endpoint)
Conclusion
Using event-driven APIs has become key to meet customer demand and provide a better user experience. Since there are several fundamental differences between REST and async APIs, using a standard API management solution may be challenging. The right API management solution should combine traditional API management capabilities with an event-driven architecture. This will provide tremendous value additions, to expand business reach and adoption.
Feature image via Pixabay.
Source: InApps.net
Let’s create the next big thing together!
Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.


















