Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a dynamic software development approach. Its goal is to swiftly craft high-quality applications using iterative processes, incorporating user feedback, building prototypes, and leveraging automation.
The future of RAD looks promising. According to Technavio, the RAD market is projected to experience a remarkable CAGR of 39.7% between 2022 and 2027. This expansion could increase the market’s size by USD 129.02 billion. The core idea behind the RAD model is to involve users right from the start of development to comprehend their needs and desires. This can be done by crafting prototypes and continuously enhancing them based on user feedback until satisfaction is reached.
To further help you understand this term, our team will delve into RAD’s history, traits, advantages, difficulties, and instances. By the end of this piece, you’ll not only grasp the distinctive features of the RAD methodology but also how it empowers teams to realize their digital ideas amidst ever-changing technology swiftly.
Let’s jump in!
Key Summary
This article from InApps Technology, authored by Julie Nguyen, provides a comprehensive overview of Rapid Application Development (RAD), a flexible, iterative software development methodology focused on delivering high-quality applications quickly. It covers RAD’s history, processes, phases, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability, citing a Technavio report projecting the RAD market to grow at a 39.7% CAGR from 2022 to 2027, increasing by USD 129.02 billion. Key points include:
- What is RAD?:
- Definition: An adaptive methodology (also called Rapid Application Building, RAB) that delivers high-quality software quickly using iterative processes, user feedback, prototyping, and automation.
- Core Principle: Treats software projects as malleable (like clay), involving users from the start to refine prototypes iteratively based on feedback, unlike rigid traditional methods.
- Comparison to Agile: RAD aligns with Agile by prioritizing speed, flexibility, and user involvement over detailed planning, reusing code and models to create prototypes rapidly.
- History of RAD:
- Origin: Introduced in 1991 by James Martin in his book Rapid Application Development, aiming to accelerate development with better quality using powerful tools.
- Context: Emerged as a response to the slow, inflexible Waterfall model, promoting teamwork and iterative development, contributing to Agile’s popularity.
- How RAD Works:
- Process: Developers collaborate with clients to define goals, identify features, and create modular prototypes. These are refined iteratively based on client feedback until the software meets expectations.
- Benefits: Resolves issues early in the design phase, minimizes risks, and enhances client satisfaction through continuous interaction.
- Four Phases of RAD:
- Requirements Planning:
- Define flexible project requirements through discussions with developers, clients, and stakeholders.
- Steps: Investigate problems, outline requirements, secure stakeholder approval.
- User Design:
- Core of RAD, involving close client collaboration to test and refine prototypes iteratively.
- Focuses on essential features, addressing issues through repeated feedback cycles.
- Construction:
- Transforms prototypes into a functional model via coding, testing, and feedback.
- Includes preparing for rapid construction, coding, and conducting unit, integration, and system testing.
- Cutover:
- Deploys the system into production with thorough testing, technical documentation, issue tracking, and final updates before launch.
- Requirements Planning:
- Advantages of RAD:
- Speed: Faster development and delivery, reducing time-to-market.
- Flexibility: Adapts to changing requirements.
- Customer Involvement: Enhances satisfaction through continuous feedback.
- Quality: Early issue detection via frequent testing.
- Risk Reduction: Incremental approach minimizes project risks.
- Communication: Fosters collaboration between developers and clients.
- ROI: Shorter cycles lead to quicker returns on investment.
- Disadvantages of RAD:
- Cost: Iterative cycles and client involvement increase expenses.
- Scalability: Less suited for large-scale or highly complex projects.
- Management Complexity: Requires skilled project management for iterative cycles.
- User Dependency: Relies on consistent user availability for feedback.
- Incomplete Features: Rapid iterations may deliver partial functionality.
- Documentation: May lack comprehensive documentation, complicating maintenance.
- Project Suitability: Best for small/medium projects with clear goals, not mission-critical systems.
- Is RAD Right for Your Project?:
- Key Questions:
- Are requirements likely to change?
- Is user feedback critical?
- Does the project benefit from quick prototyping and iterative progress?
- Is it small/medium-sized with clear goals?
- Is the team skilled and collaborative?
- Suitability: Ideal if most answers are “yes,” but user availability and internal opinions can impact iterations.
- Key Questions:
- InApps Insight:
- InApps Technology leverages RAD’s principles for agile development, using Microsoft’s Power Platform and Azure, with Power Fx for low-code prototyping and Azure Durable Functions for scalable workflows.
- Integrates Node.js, Vue.js, GraphQL APIs (e.g., Apollo), and Azure to deliver rapid, user-focused solutions, targeting startups and enterprises with Millennial-driven expectations.
What is Rapid Application Development (RAD)?
Rapid application development (RAD), or rapid application building (RAB), is an adaptive software development methodology aiming to deliver high-quality applications ‘in a short time frame’ using iterative and incremental processes, user feedback, prototyping, and automation.
RAD is based on the principle that the best way to understand the requirements and expectations of the users is to involve them in the development process from the beginning. This helps to test and refine the prototypes until they are satisfied.
Many people confuse RAD with a specific model, but the main idea of RAD is to treat software projects like modeling clay, not unyielding steel. Instead of sticking to a strict plan, it involves creating a prototype of the software and then improving it based on user feedback. The development team will repeat this process until the software meets all the client’s requirements.
The History of Rapid Application Development
In 1991, James Martin, a well-known figure in the field of IT engineering, wrote a book about a new way of creating software. He called it “Rapid Application Development,” or RAD for short. James described RAD as a methodology for accelerating software development with better quality than traditional methods. Moreover, RAD takes advantage of new and powerful software tools.
Before RAD, people mostly used the waterfall model to make software. But, this method was inflexible, slow, and risky, especially for complex and changing projects. RAD came as a response to this and offered a different way. It’s a faster, more teamwork-oriented approach to making working software instead of just following a fixed plan.
Even though these Agile ideas were not wholly new, RAD really helped to make them more popular in the world of software development.
What is RAD in agile?
Rapid Application Development (RAD) represents a fast-paced agile approach aiming to deliver high-quality results promptly. Unlike the Waterfall model, RAD prioritizes practical steps over intricate planning. It reuses established code, models, and proven procedures to construct new software prototypes. This model brings flexibility, adaptability, and time savings to web applications and software development. It’s beneficial when creating new apps quickly.
On the other hand, agile delivery techniques address the need for elegant client service in the IT industry, driving business modernization. The aim is to develop dynamic, adaptable projects while reshaping the mindsets of managers and internal teams.
RAD devises processes that emphasize speed and flexibility, blending them with Agile’s adaptable methodology.
Agile leverages innovative software to enhance the development process effectively. It combines professionals, tools, and active team involvement to create efficient products. Customers might receive basic features before the project is delivered in stages or segments.
How does Rapid Application Development Work?
In the rapid application development approach, the software development team collaborates with the client (who could be from within the organization) to outline the project’s goals. The client shares what they want the software to achieve, any concerns, and any problems it should solve. Then, the development team reviews these inputs and finalizes a list of features to include in the project.

Once the feature list is settled, the developers create prototypes organized into modules. These prototypes can be refined multiple times to incorporate feedback from the client and to adapt to any changes in requirements. This refinement continues until the software meets the client’s expectations.
The RAD process facilitates swift progress by identifying and resolving most challenges and roadblocks during the design phase before they occur.
The ongoing interaction between the client and the development team enhances client satisfaction. This is why RAD stands out as a software development approach that minimizes the risks tied to software creation and ensures the delivery of high-quality software within a short timeframe.
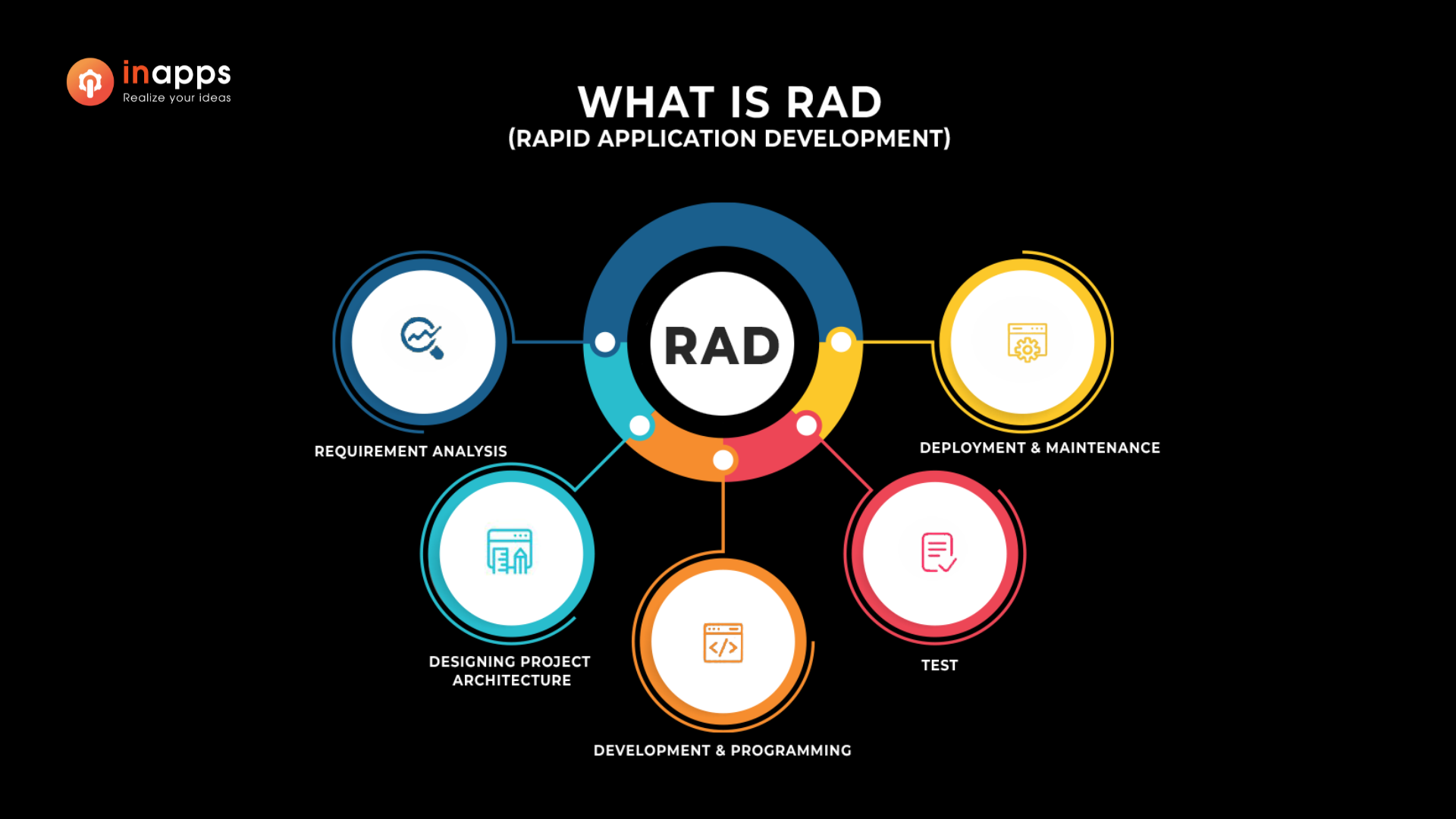
How Many Phases of RAD?
RAD consists of four main phases. Developers and users collaborate during each stage to establish, plan, construct, examine, and introduce the application. These stages don’t occur in a strict order – instead, they overlap and repeat as necessary.
Here are the four basic steps of RAD:
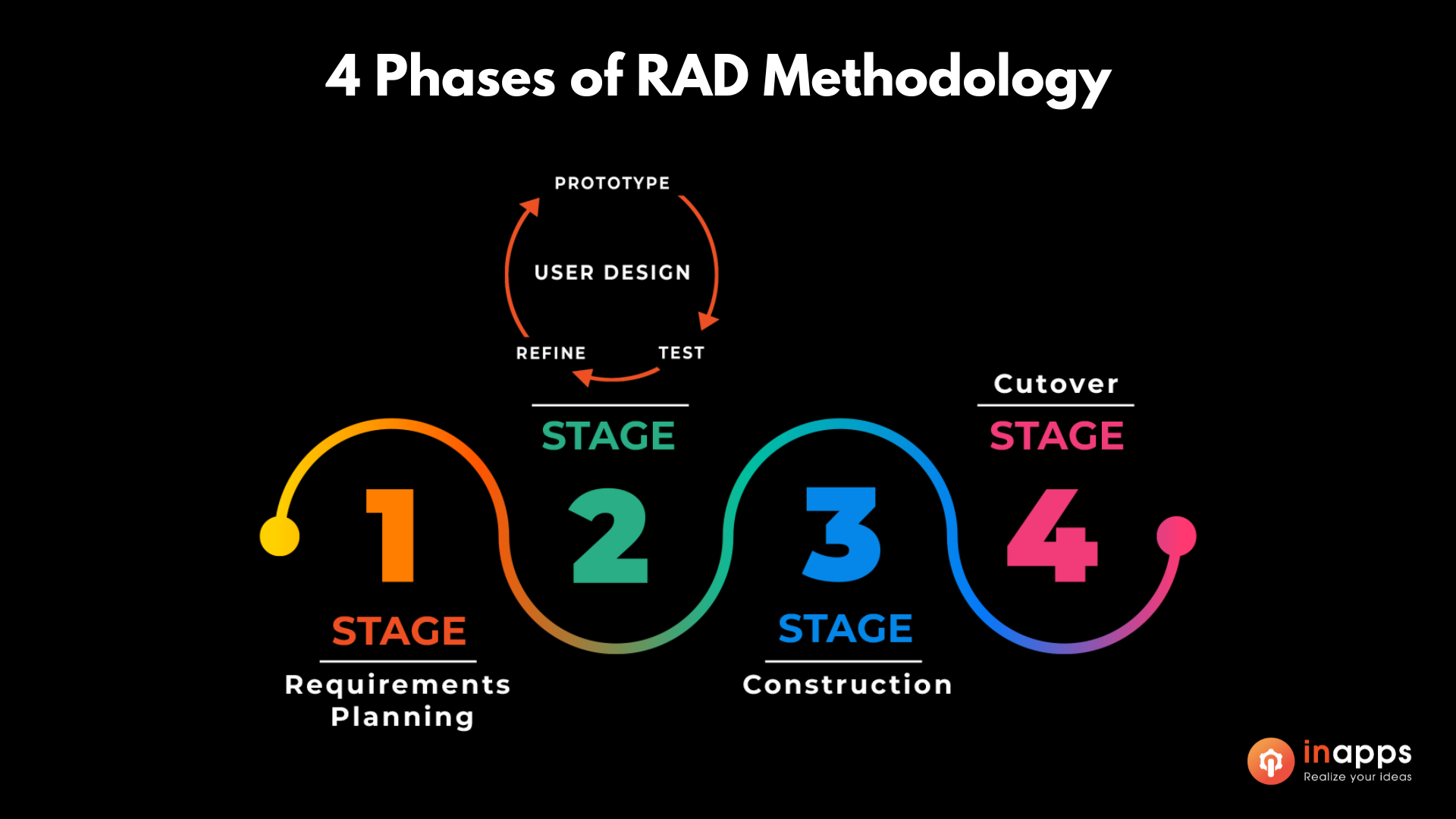
Requirements planning
Instead of making you invest months in crafting detailed specifications with users, RAD kicks off by outlining a flexible set of requirements. These requirements are kept flexible because one of the core tenets of rapid application development is the freedom to modify them anytime in the process.
In this phase, developers, clients (software users), and team members engage in discussions to establish project goals and expectations. They also identify existing problems and potential issues that should be tackled during development.
The essential steps in this stage include:
- Investigating the current problem.
- Outlining project requirements.
- Securing approval from all stakeholders on the final requirements.
2. User design
This is the heart of the RAD methodology, which makes it different from other project management approaches. In this phase, clients collaborate closely with developers to ensure their needs are met throughout the design process. It’s like tailoring software development, where users can try out each product version in every stage to ensure it meets their expectations.

Any issues and glitches are ironed out through a repetitive process. The developer creates a prototype, the client tests it, and then they discuss what worked and what didn’t.
These prototypes often focus on showcasing the essential features, and that’s completely normal. The final product only comes together in the finalization stage when the client and developer agree on the finished product.
3. Construction
Phase 3 transforms the prototypes and beta systems from the user design phase into a functioning model. During this stage, the software development team, which includes programmers, coders, testers, and developers, collaborates to ensure everything runs smoothly and meets the client’s expectations and goals.
Feedback and reviews play a vital role at this point, where most issues, bugs, and changes are addressed. This stage can be lengthy, especially if clients alter their requirements or provide extensive feedback.
This phase can be broken down into these smaller steps:
- Preparing for rapid construction
- Developing programs and applications
- Writing code
- Conducting unit, integration, and system testing
4. Cutover
The last step in RAD is putting the system into action in a real working environment. This means doing thorough testing to ensure it can handle many users, making technical documents, keeping track of problems, making any last changes, and pretending to use the system to see how it works. Teams also work on fixing any issues and doing one final round of updates and maintenance before it’s officially launched.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Rapid Application Development Methodology
These steps might make application development seem like a good choice for all projects, but that’s not entirely true. RAD software works well for small teams and fast projects, but it doesn’t solve every problem.
Here are some pros and cons of using rapid application development:
| Advantages of RAD model | Disadvantages of RAD model |
| Rapid development: RAD allows for faster software development and delivery, reducing time-to-market. | Higher cost: The iterative nature of RAD can be more expensive due to the need for frequent client involvement and continuous testing. |
| Flexibility: RAD is highly adaptable to changes in requirements, making it suitable for projects with evolving needs. | Limited scalability: RAD may not be ideal for large-scale projects or systems that require significant scalability. |
| Customer involvement: RAD emphasizes customer involvement and feedback throughout the development process, leading to higher customer satisfaction. | Complex management: Managing iterative cycles and multiple prototypes can be challenging and requires skilled project management. |
| Better quality: Frequent testing and feedback help identify and fix issues early in development, leading to higher software quality. | Dependence on user availability: RAD relies heavily on the availability of users for feedback and collaboration, which can be a constraint. |
| Reduced risk: The incremental approach and continuous testing in RAD minimise project risks by identifying issues early and allowing for corrective action. | Incomplete functionality: Rapid iterations may result in software delivery with incomplete features or functionalities. |
| Improved communication: RAD encourages close collaboration between developers, clients, and end-users, fostering better communication and understanding of requirements. | Limited documentation: Due to the focus on prototypes and iterations, RAD may result in inadequate documentation, making maintenance and future development challenging. |
| Faster ROI: The shorter development cycles in RAD can lead to quicker returns on investment (ROI) for the project stakeholders. | Not suitable for all projects: RAD is best suited for projects with well-defined and stable requirements; it may not work well for highly complex or mission-critical systems. |
The Bottom Line: Is RAD the Right Model for You?
When deciding if the RAD model is a good fit for your project, consider these questions:
- Will your project’s requirements likely change?
- Is user feedback crucial for development?
- Can your project benefit from quick prototyping and step-by-step progress?
- Is your project small or medium-sized with clear goals?
- Do you have a skilled, teamwork-oriented team ready for RAD’s demands?
If most answers are “yes,” the RAD model could be a smart choice for your project. However, remember that RAD relies on continuous user feedback, which might not always be easy to obtain. This means that internal opinions could affect iterations.
In summary, the Rapid Application Development model provides a flexible, collaborative, and efficient approach to software development. By understanding its pros and cons, you can make an informed decision about using this method in your projects. Thank you for reading!
Let’s create the next big thing together!
Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.