- Home
- >
- Software Development
- >
- Using Private Data Collections in Hyperledger Fabric – InApps Technology 2022
Using Private Data Collections in Hyperledger Fabric – InApps Technology is an article under the topic Software Development Many of you are most interested in today !! Today, let’s InApps.net learn Using Private Data Collections in Hyperledger Fabric – InApps Technology in today’s post !
Read more about Using Private Data Collections in Hyperledger Fabric – InApps Technology at Wikipedia
You can find content about Using Private Data Collections in Hyperledger Fabric – InApps Technology from the Wikipedia website
The Linux Foundation sponsored this post.

Chris Gabriel
Chris is Founder and CEO of Hyperchain Labs.
It’s becoming increasingly important to use blockchain in business and government. As I write this, the global COVID-19 pandemic is raging across the globe. Everyone from individuals, businesses and governments are having to accelerate their digital transformations from original timelines of years to revised timelines of months or even weeks. Businesses, governments and their processes are like heart arteries that slowly clogged over a long period of time from a poor diet and a lack of exercise. Suddenly, the host is required to run a half-marathon in a few weeks, and the arteries are not prepared for it.
Permissioned blockchain is a business process and contractual truth-teller and can be used for such things as contact tracing without exposing personal information (private data, as we will discuss below), voting in national elections with verified identities (from anywhere), and payment distributions at scale (avoiding the current state of poorly maintained state unemployment benefit payment systems running on 1990s technologies). In short, I am convinced that blockchain technologies will become increasingly important to businesses and governments in a post-COVID-19 environment, as they reflect on what technologies will be required to address these and other issues in the future.
What Is Hyperledger Fabric?
Hyperledger Fabric is an enterprise-grade permissioned blockchain that is used between trusted parties to remove friction from common business processes, by using cryptographic identity management, smart contracts, and an immutable distributed ledger as a replacement for disparate ERP systems, paper contracts, emails, phone calls, and manual human intervention points. Hyperledger Fabric is one of many open source blockchain projects hosted by the Linux Foundation.
What Are Private Data Collections and Why Use Them?
Private data collections are predefined data collections (usually in JSON format) that enable companies within a Hyperledger Fabric blockchain consortium to keep certain transactional data private, while still allowing for consensus to be reached among all required nodes.
Private data collections consist of two primary parts:
- the actual private data; data is stored in a private database on the peer nodes of authorized organizations and is accessed from chaincode on these authorized peers; and
- a hash of that private data; endorsed, ordered, and written to the ledgers of every peer on the channel.
The business case for using permissioned blockchain is that you get the efficiency of scale and network effect by having all of your competitors, suppliers and regulators on the same blockchain network. There are two primary business benefits to this approach: first, at least some of the benefits of the network effect accrue to all of the members of the network, not just a few; and, second, using private data collections ensures that network members do not compromise a competitive advantage they may have, by exposing sensitive data to network members that do not have a need to see it but are still required to have their nodes achieve consensus.
Figure 1 shows an example of what a private data collection in JSON format looks like for an asset collection:

Figure 1
Note that the “policy” in “collectionAssets” allows for members of Org1 OR Org2 to access and transact on the data, but the “policy” in the “collectionAssetPrivateDetails” only allows for members of Org1 to access and transact on the private data details.
Other fields of interest in the collection are:
- requiredPeerCount, which specifies the number of peers required to disseminate the private data as a chaincode endorsement condition.
- maxPeerCount, the number of peers the endorsing peer will attempt to distribute data to for redundancy purposes.
- blockToLive, which specifies how long sensitive data should live on the private database of the peer in terms of blocks.
- memberOnlyRead, which, when set to true, indicates that peers automatically enforce that only clients belonging to one of the collection member organizations are allowed to read access to private data.
With regard to blockToLive, it is important to note that the data lives until it gets purged after reaching the required block count. You do, however, have the option of keeping private data indefinitely by setting blockToLive to “0.”
Figure 2 shows a graphic visualization of the concept above. Org2 can query data related to asset1, which is owned by Org1, but remember that the policy for the private data collection only allows for those members of Org1 to gain access to the private data details which are kept from Org2.
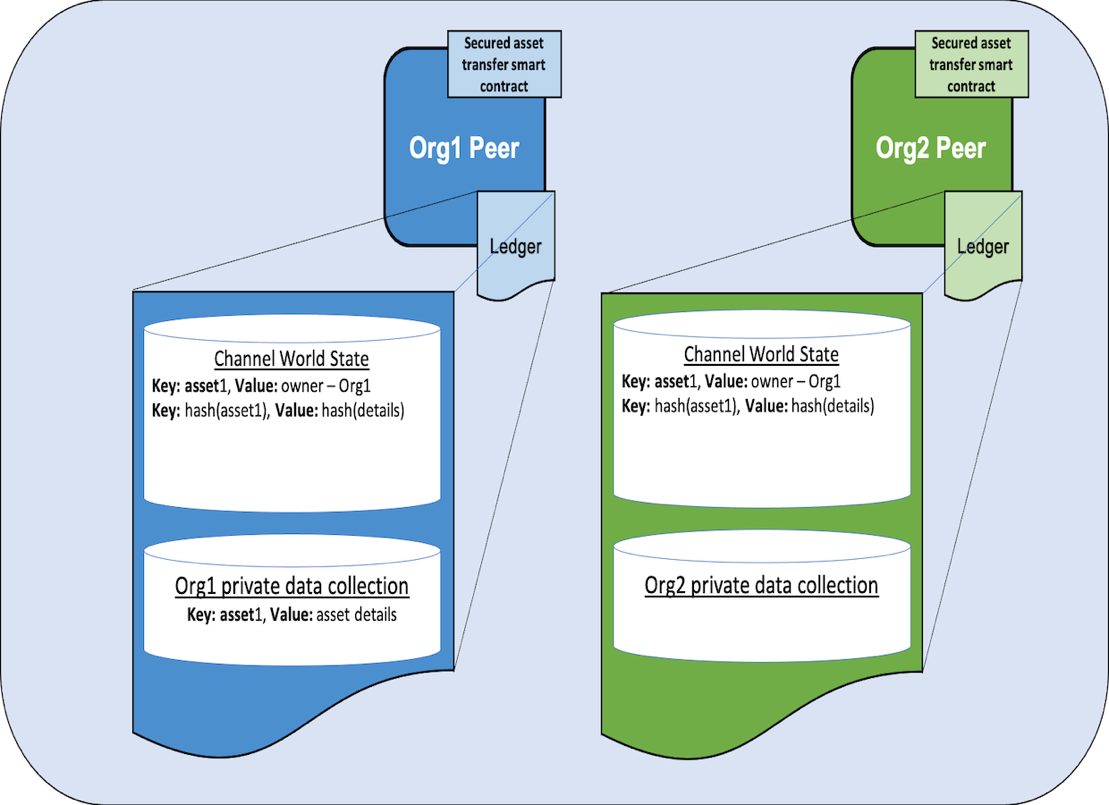
Figure 2
As adoption of blockchain technologies begins to gain more traction among businesses and government agencies, the need for robust privacy mechanisms like private data in Hyperledger Fabric will become increasingly more important. When all members of a blockchain network are incentivized by sharing in the overall benefit of being in a business consortium with transactional outputs that can be verifiably trusted, we will begin to see the end of the traditional technology stacks that business and government have transacted on for decades.
To get more detail on how private data works in Hyperledger Fabric permissioned blockchain networks, check out this tutorial on “Using Private Data in Fabric.” There are multiple Hyperledger Fabric tutorials available that cover almost all aspects of how to deploy Hyperledger Fabric enterprise-grade blockchain networks. You can also find the Hyperledger Fabric code on Github.
List of Keywords users find our article on Google:
| hyperledger fabric |
| hyperledger fabric private data example |
Source: InApps.net
Let’s create the next big thing together!
Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.


















